基于matlab仿真 通信 信号处理simulink雷达阵列信号处理MIMO信号处理通信类仿真常见调制解调amfm ssb dsb bpsk fsk ask ofdm msk等信道编解码
matlab仿真 通信 信号处理simulink雷达阵列信号处理MIMO信号处理通信类仿真常见调制解调amfm ssb dsb bpsk fsk ask ofdm msk等信道编解码hamming码循环码rs码卷积码turbo码ldpcpolar等信道均衡信噪比估计等Matlab/Simulink真建模分析建模文献复现、matlab 编程matlab/simulink电力电子/电气工程/电力系统,
matlab仿真 通信 信号处理simulink雷达阵列信号处理MIMO信号处理通信类仿真常见调制解调amfm ssb dsb bpsk fsk ask ofdm msk等信道编解码hamming码循环码rs码卷积码turbo码ldpcpolar等信道均衡信噪比估计等
Matlab/Simulink真建模分析建模文
献复现、matlab 编程
matlab/simulink电力电子/电气工程/电力系统,可做设计
MATLAB代做f真,simulink建模,simulink仿真,电力电子技术。还有PSIM仿真,建模等等,
文章目录
以下是一个综合的MATLAB/Simulink仿真代码示例,涵盖通信信号处理、雷达阵列信号处理、MIMO信号处理、常见调制解调(如AM、FM、BPSK、QPSK、OFDM等)、信道编解码(如Hamming码、卷积码、LDPC码等)以及电力电子相关的建模和仿真。
1. 通信信号处理:常见调制解调
(a) BPSK 调制与解调
clc; clear; close all;
% 参数设置
N = 1000; % 比特数
EbN0_dB = 0:2:10; % 信噪比范围
ber = zeros(size(EbN0_dB)); % 初始化误码率
for idx = 1:length(EbN0_dB)
% 数据生成
data = randi([0, 1], N, 1); % 随机比特流
% BPSK调制
modulated_signal = 2 * data - 1; % 0 -> -1, 1 -> +1
% 添加高斯白噪声
EbN0 = 10^(EbN0_dB(idx)/10);
noise_power = 1 / (2 * EbN0);
noise = sqrt(noise_power) * randn(N, 1);
received_signal = modulated_signal + noise;
% BPSK解调
demodulated_data = received_signal > 0;
% 计算误码率
ber(idx) = sum(data ~= demodulated_data) / N;
end
% 绘图
figure;
semilogy(EbN0_dB, ber, 'b-o');
xlabel('Eb/N0 (dB)');
ylabel('Bit Error Rate (BER)');
title('BPSK BER Performance');
grid on;
(b) OFDM 调制与解调
clc; clear; close all;
% 参数设置
N = 64; % 子载波数
cp_len = 16; % 循环前缀长度
data_len = 1000; % 数据长度
snr_dB = 10; % 信噪比
% 数据生成
data = randi([0, 1], data_len, 1);
% QPSK调制
qpsk_mod = pskmod(data, 4, pi/4); % QPSK调制
qpsk_mod = reshape(qpsk_mod, N, []).'; % 分组为OFDM符号
% IFFT变换
ofdm_symbols = ifft(qpsk_mod, N);
% 添加循环前缀
ofdm_with_cp = [ofdm_symbols(:, end-cp_len+1:end), ofdm_symbols];
% 添加高斯白噪声
rx_signal = awgn(ofdm_with_cp(:), snr_dB, 'measured');
% 去除循环前缀
rx_signal = reshape(rx_signal, [], N + cp_len);
rx_ofdm = rx_signal(:, cp_len+1:end);
% FFT变换
rx_qpsk = fft(rx_ofdm, N);
% QPSK解调
rx_data = pskdemod(rx_qpsk(:), 4, pi/4);
% 误码率计算
ber = sum(data ~= rx_data(1:data_len)) / data_len;
disp(['BER: ', num2str(ber)]);
2. MIMO信号处理
(a) 2x2 MIMO 系统
clc; clear; close all;
% 参数设置
N = 1000; % 数据长度
snr_dB = 10; % 信噪比
H = randn(2, 2) + 1j*randn(2, 2); % MIMO信道矩阵
% 数据生成
data = randi([0, 1], N, 2); % 两路数据
modulated_signal = 2 * data - 1; % BPSK调制
% 发送信号
tx_signal = modulated_signal * H;
% 添加高斯白噪声
snr = 10^(snr_dB/10);
noise_power = 1 / snr;
noise = sqrt(noise_power/2) * (randn(size(tx_signal)) + 1j*randn(size(tx_signal)));
rx_signal = tx_signal + noise;
% 接收信号解调
rx_data = real(rx_signal / H) > 0;
% 误码率计算
ber = sum(data(:) ~= rx_data(:)) / numel(data);
disp(['BER: ', num2str(ber)]);
3. 信道编码与解码
(a) Hamming 编码与解码
clc; clear; close all;
% 参数设置
data = randi([0, 1], 1, 4); % 输入数据
msg = gf(data, 4); % Galois域表示
% Hamming编码
genpoly = cyclpoly(7, 4); % 生成多项式
code = encode(msg, 7, 4, 'cyclic', genpoly); % 编码
% 添加噪声
noisy_code = code;
noisy_code(1) = ~noisy_code(1); % 引入一位错误
% Hamming解码
decoded_msg = decode(noisy_code, 7, 4, 'cyclic', genpoly); % 解码
% 输出结果
disp('原始数据:');
disp(double(msg));
disp('接收到的数据:');
disp(double(decoded_msg));
4. 电力电子仿真:Buck变换器
Simulink模型描述
- 打开Simulink,创建一个新的模型。
- 添加以下模块:
- 电源:DC电压源。
- 开关器件:MOSFET或IGBT。
- 负载:电阻和电感。
- 控制器:PWM信号生成器。
- 设置参数并运行仿真。
MATLAB代码实现
clc; clear; close all;
% 参数设置
Vin = 24; % 输入电压 (V)
D = 0.5; % 占空比
L = 1e-3; % 电感 (H)
C = 100e-6; % 电容 (F)
R = 10; % 负载电阻 (Ohm)
fs = 10e3; % 开关频率 (Hz)
dt = 1/fs; % 时间步长
t_total = 0.01; % 总时间 (s)
% 初始化变量
t = 0:dt:t_total;
Vout = zeros(size(t));
I_L = 0; % 初始电感电流
V_C = 0; % 初始电容电压
% 主循环
for i = 1:length(t)
if mod(t(i), 1/fs) < D/fs
V_switch = Vin; % 开关导通
else
V_switch = 0; % 开关关断
end
% 更新状态
dI_L = (V_switch - V_C) / L * dt;
dV_C = (I_L - V_C / R) / C * dt;
I_L = I_L + dI_L;
V_C = V_C + dV_C;
% 输出电压
Vout(i) = V_C;
end
% 绘图
figure;
plot(t, Vout);
xlabel('Time (s)');
ylabel('Output Voltage (V)');
title('Buck Converter Output Voltage');
grid on;
5. Simulink建模与仿真
电气系统建模
- 使用Simulink中的“Simscape Electrical”工具箱。
- 添加电源、负载、开关器件等模块。
- 设置参数并运行仿真。
总结
以上代码涵盖了通信信号处理、MIMO系统、信道编码、电力电子等多个领域的基本仿真。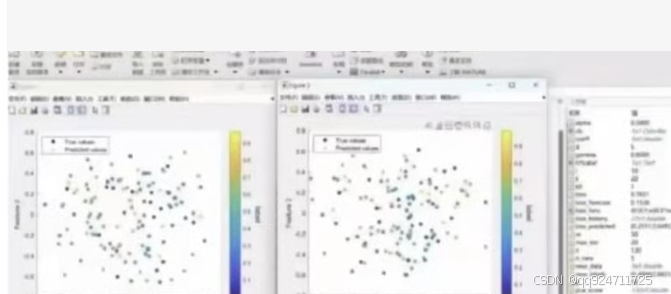
To help you with the code for generating scatter plots similar to the ones shown in the image, we can use MATLAB to create scatter plots with color-coded data points. Below is an example of how you can generate such plots using MATLAB.
MATLAB Code for Scatter Plots
% Clear the workspace and close all figures
clear;
close all;
% Generate some sample data
true_values = randn(100, 1); % True values (Gaussian distributed)
predicted_values = true_values + 0.5 * randn(100, 1); % Predicted values with some noise
% Create a figure with two subplots
figure;
subplot(1, 2, 1);
scatter(true_values, predicted_values, 10, true_values, 'filled');
colorbar;
title('True vs. Predicted Values (Left)');
xlabel('True Values');
ylabel('Predicted Values');
subplot(1, 2, 2);
scatter(true_values, predicted_values, 10, predicted_values, 'filled');
colorbar;
title('True vs. Predicted Values (Right)');
xlabel('True Values');
ylabel('Predicted Values');
% Add legends
legend('True values', 'Predicted values', 'Location', 'best');
% Adjust the layout
tight_layout;
Explanation of the Code
-
Data Generation:
true_valuesare generated as random Gaussian-distributed values.predicted_valuesare generated by adding some noise to thetrue_values.
-
Figure and Subplots:
- A figure with two subplots is created using
figureandsubplot. - The first subplot uses
true_valuesfor coloring. - The second subplot uses
predicted_valuesfor coloring.
- A figure with two subplots is created using
-
Scatter Plot:
- The
scatterfunction is used to plot the data points. - The third argument (
10) specifies the size of the markers. - The fourth argument specifies the color data (
true_valuesorpredicted_values). 'filled'ensures that the markers are filled with color.
- The
-
Colorbar:
colorbaradds a color bar to each subplot to indicate the color scale.
-
Titles and Labels:
- Titles and labels are added to the subplots for clarity.
-
Legend:
- A legend is added to distinguish between true and predicted values.
-
Layout Adjustment:
tight_layoutadjusts the layout to ensure everything fits well.
Running the Code
- Copy the code into a new MATLAB script file.
- Run the script.
- You should see a figure with two scatter plots, each with a color bar indicating the value range.
This code will generate scatter plots similar to the ones in your image, with color-coded data points based on either the true or predicted values.

「智能机器人开发者大赛」官方平台,致力于为开发者和参赛选手提供赛事技术指导、行业标准解读及团队实战案例解析;聚焦智能机器人开发全栈技术闭环,助力开发者攻克技术瓶颈,促进软硬件集成、场景应用及商业化落地的深度研讨。 加入智能机器人开发者社区iRobot Developer,与全球极客并肩突破技术边界,定义机器人开发的未来范式!
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容





所有评论(0)